Description
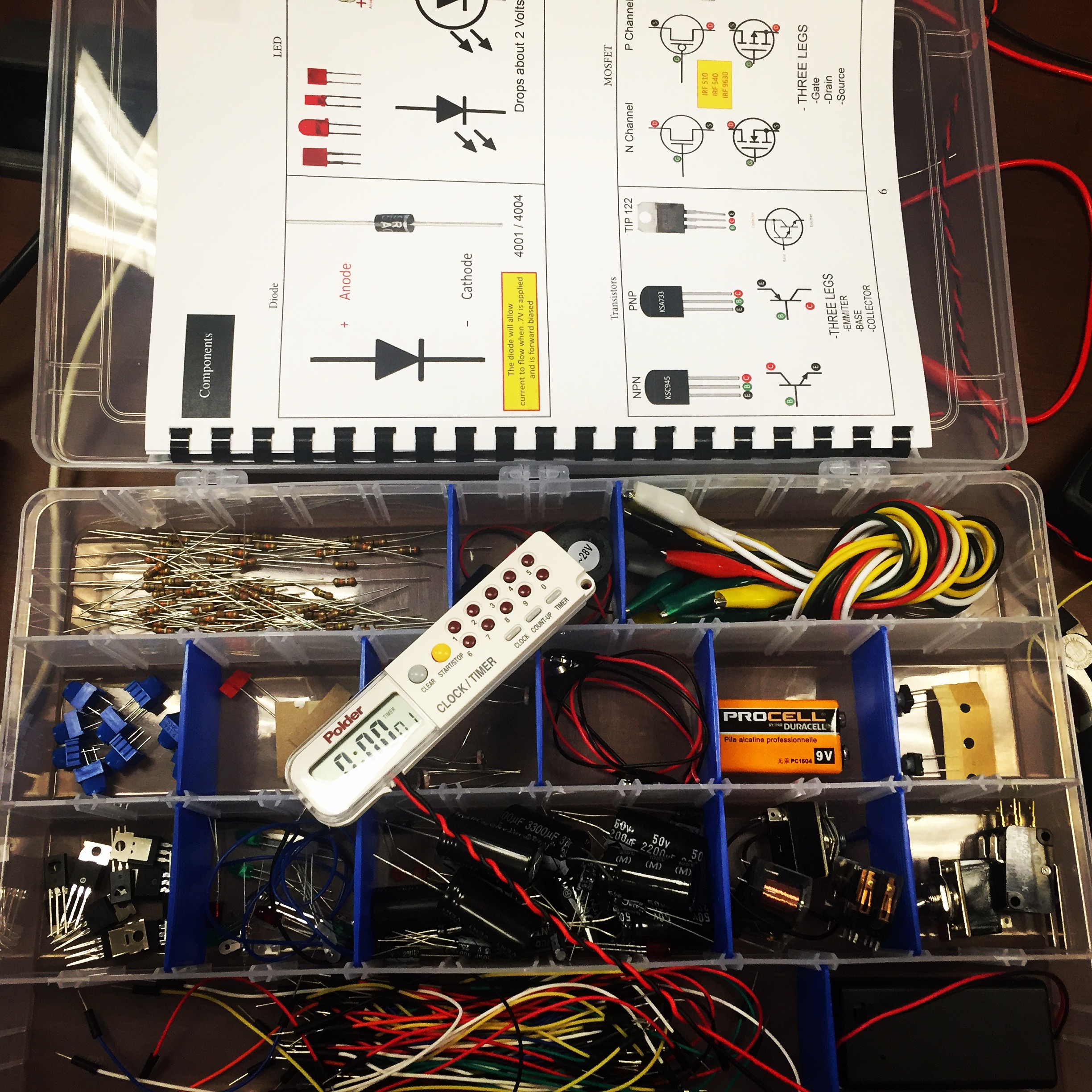
This 40hr EOD Electronics Course reveals how modern electronics offer the terrorist a broad range of options for device design and construction. Assuming no previous knowledge of electronics, participants gain a practical understanding of devices such as collapsing circuits (traditional and solid state), modification of commercial technologies for use in IEDs, and remote-controlled IEDs (RCIEDs), including dual tone multi-frequency (DTMF), and other coding systems. The course begins with an outline of electrical theory and Ohm’s Law, followed by an introduction to a wide variety of electronic components. Components will be introduced as schematics, physical components, radiographs or as post blast photographs as needed to reinforce training topics associated with EOD Tasks. Emphasis is placed on the characteristics of electronic components and circuits that make them attractive to the terrorist and the characteristics that often cause training devices to fail. Students learn primarily by building circuits and soldering those circuits together on provided printed circuit boards.
Training Objectives:
|
Understand the fundamentals of Electronic Theory
|
|
|
|
Schedule of Events:
Day 1- DC Theory Lecture and Lab (Resistors Batteries, Capacitors and switches)
Lab: Breadboard simple circuits and test with supplied multimeter
Solder breadboard leads to switches
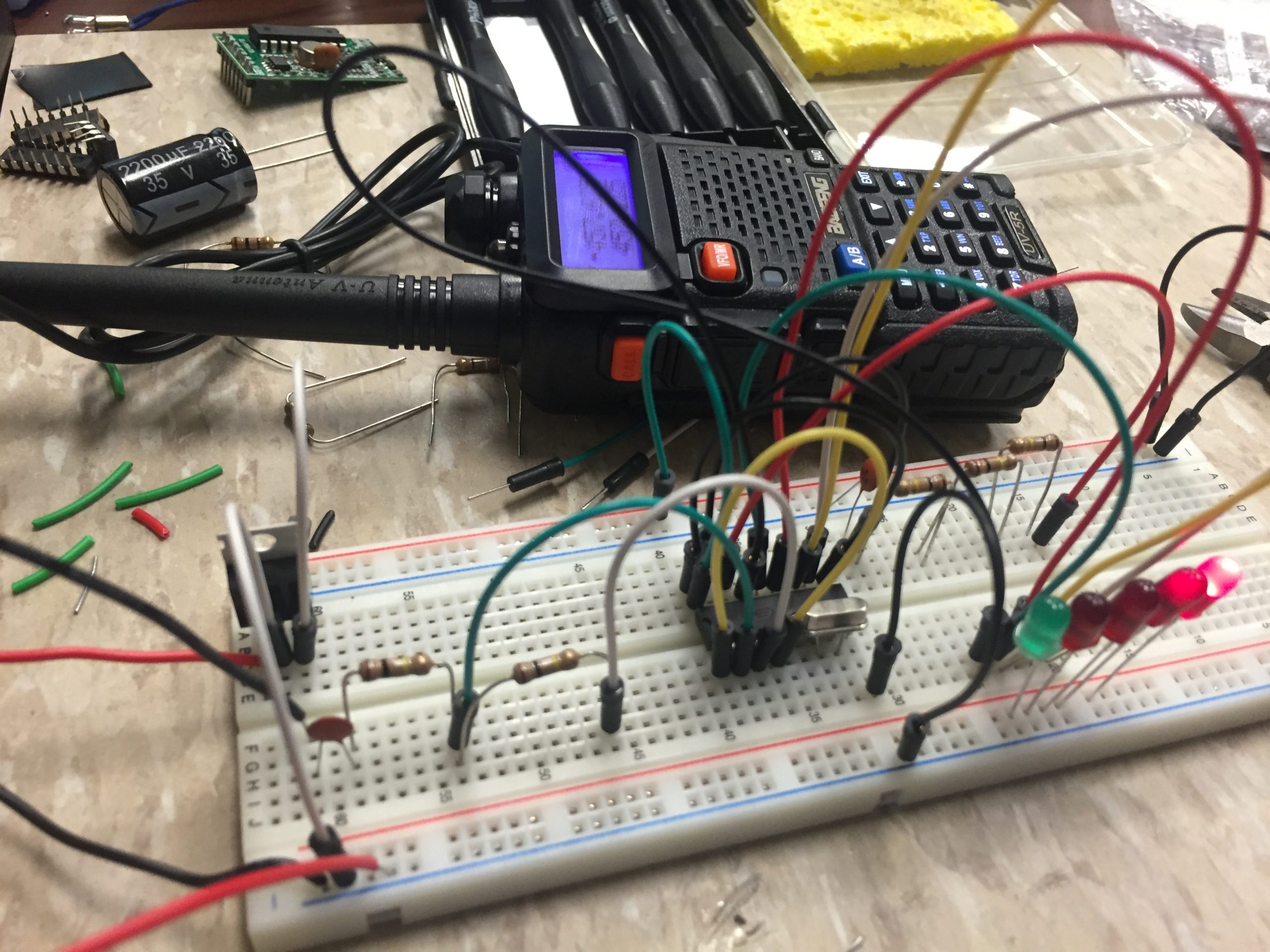
Day 2- Relays, Diodes, Transistors, MOSFETs, and SCRs Lecture and Lab
Labs: Breadboard 5 historical IEDs using supplied components from lecture
Day 3-Logic Chips and RCIED Circuits
Labs: Build RFT-2 on supplied PCB
Build DTMF PIC IED Circuit Board and interface with COTS radio (Similar to DTMF-11)
Day 4- Programming Concepts and Arduino Applied to IEDs
Labs: Arduino Light Meter (from source code)
Arduino PIR Counter
Day 5- Capstone IED Team Build
Students will split into teams of 4 and build a modern microcontroller based RCIEDs with sensors. Source code will be provided.
Deliverables:
- Lab kit (Breadboard, Multimeter, Soldering Iron, Parts Kit, COTs timer and DTMF Radio, and Arduino boards)
- Student Training guide with schematics & diagrams
- CAD files and source code (from the labs)
- Certificate of Completion